By Bhavishyaa Vignesh, 13
CAGIS Teen Ambassador
Recently, I did an activity where I called out the first names of famous scientists in front of a crowd. The audience was asked to shout out each scientist’s last name in response. I noticed that when I called out famous women who had accomplished remarkable things in STEM, the crowd was pretty silent because they didn’t know who these amazing women were. One of these scientists was Dorothy Hodgkin and I want to tell you a bit about her so that the next time I run that activity, someone will call out her last name!
So, who was Dorothy Hodgkin?
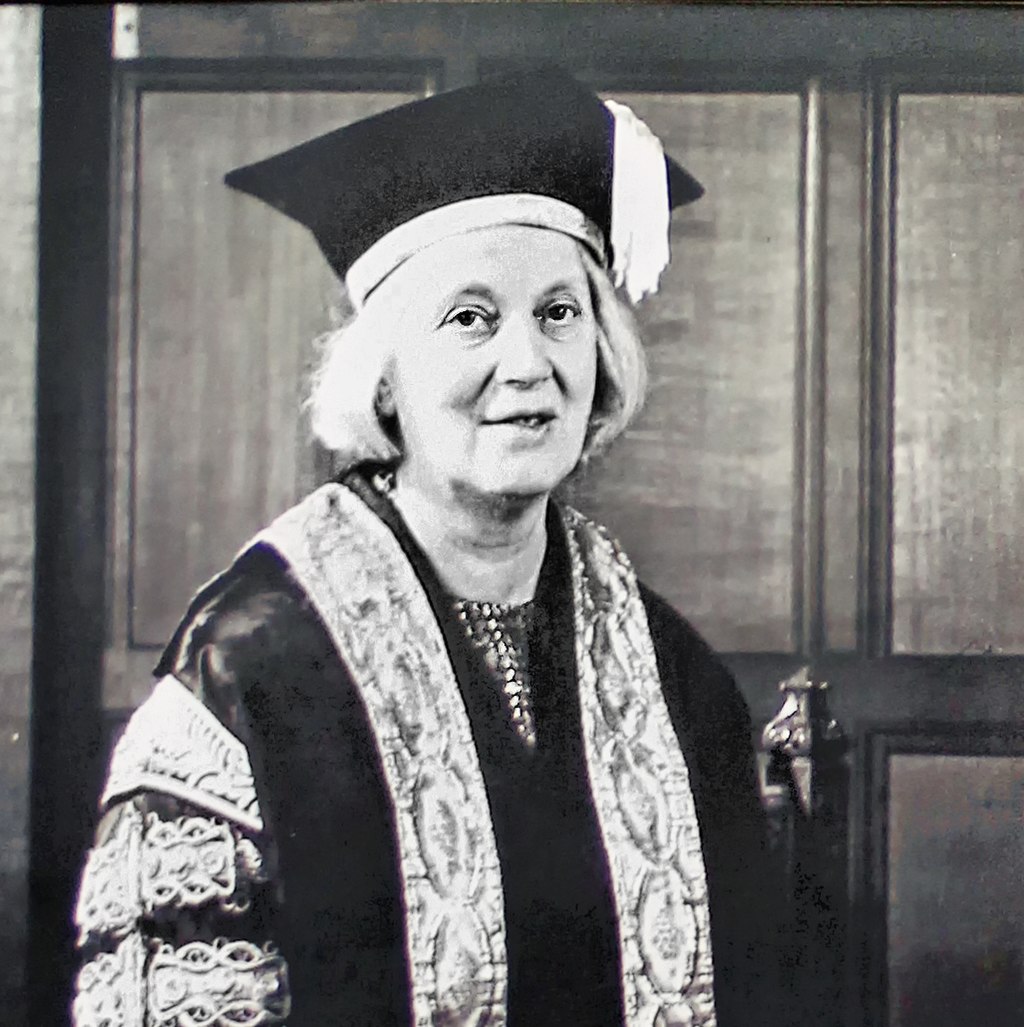
Dorothy Hodgkin was an English chemist. When she was very young, she showed an interest in chemistry and crystal formation. This interest was nurtured by her parents and her teachers at school. In fact, Dorothy was even allowed to join the boys for chemistry class which was uncommon at the time. Her early love of chemistry is what led her to pursue the field at university.
What did Dorothy discover?
In 1964, Dorothy Hodgkin won the Nobel Prize. She was the third woman to have received this honour and was awarded the Prize for helping to discover the structure of penicillin and Vitamin B12. To do so, she used a method called crystallography. This technique uses X-ray images to show scientists the structure of a biomolecule. Hodgkin worked for many years with other scientists, collecting and studying these images. Her incredible discoveries became the foundation for other scientific breakthroughs. For example, later in her career, Hodgkin discovered the structure of insulin which led to new treatments for diabetes.

Some of Dorothy Hodgkin’s awards and recognitions include:
Nobel Prize in Chemistry (1964): Dorothy was awarded the Nobel Prize for her determinations by X-ray techniques of the structures of important biochemical substances. This was primarily in recognition of her work on the structure of vitamin B12.
Order of Merit (1965): Dorothy was appointed to the Order of Merit by Queen Elizabeth II. The Order of Merit is a highly prestigious honor in the United Kingdom, recognizing distinguished service in the armed forces, science, art, literature, or for the promotion of culture.
Copley Medal (1976): Awarded by the Royal Society, the Copley Medal is one of the oldest and most prestigious scientific awards in the world. Dorothy received it for her exceptional contributions to scientific research, particularly in the field of X-ray crystallography.
Lomonosov Gold Medal (1982): This award is presented by the Russian Academy of Sciences and is given for outstanding achievements in the natural sciences and the humanities. Dorothy was recognized for her significant contributions to chemistry.
“The pursuit of knowledge requires accepting that there will always be more to learn.” – Dorothy Hodgkin
Dorothy Hodgkin has been a huge inspiration to me and she is a constant reminder that I can achieve anything at any age if I put my mind to it.
About the Auhor
Hey there, I’m Bhavi. I’m a 13-year-old Space Tech & AI enthusiast. I’ve been a part of CAGIS since I was seven years old, and I love it. I’ve spoken on a TEDx about Breaking Barriers and Girls in STEM. I’ve taught 500+ kids around the world about coding, space, and 3D modeling, and I was the winner of the 2023 BrainHack Hackathon.
Main Image: University of Bristol, CC BY-SA 2.5 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5>, via Wikimedia Commons